The realistic material
The first and default material type is realistic. It is energetically equilibrated.
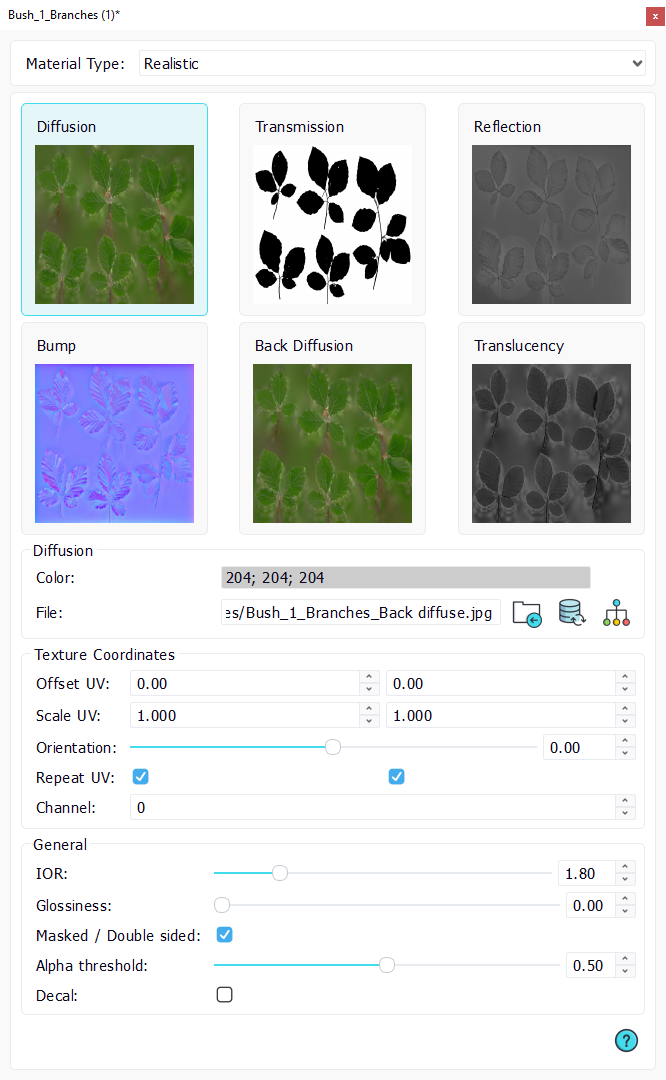
The realistic material panel
The energy preservation model
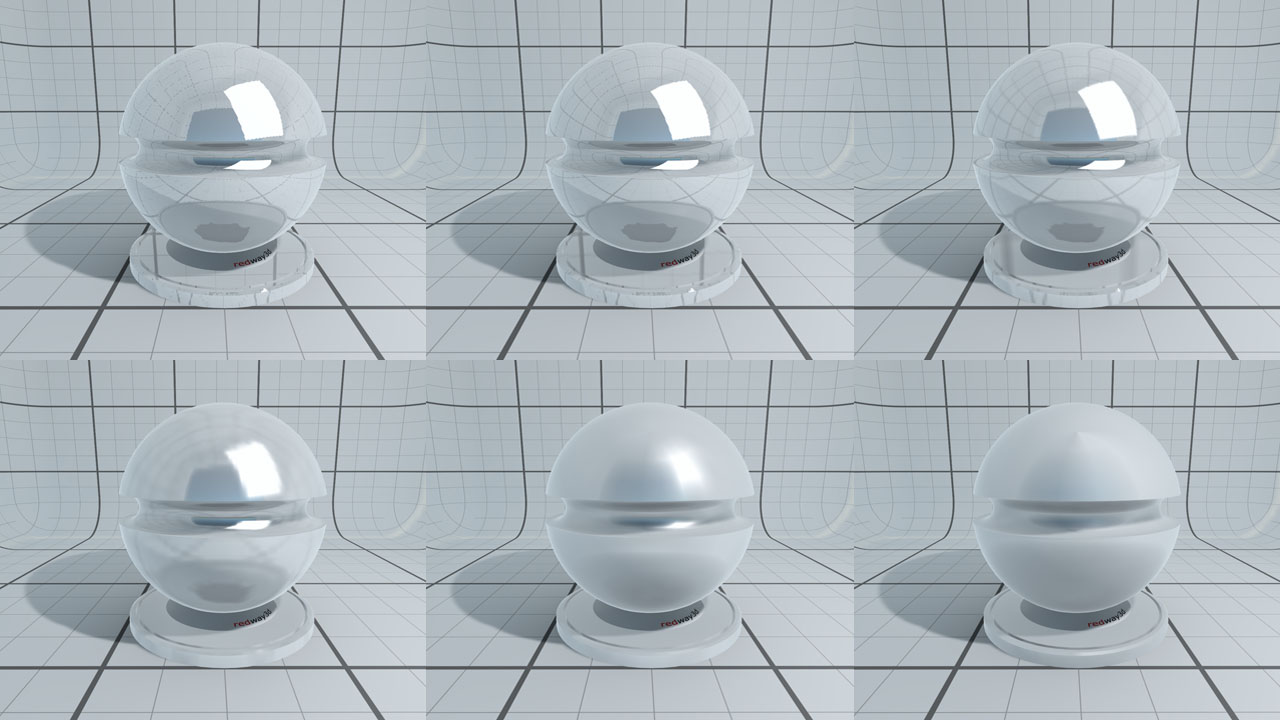
The shading model uses three basic inputs:
- Diffusion: the material base color used in a Lambertian equation.
- Reflection: how much the material reflects its environment.
- Transmission: opacity of the material.
These three inputs are involved in the energy preservation rule: the sum of the diffusion + reflection + transmission terms is always lower than or equal to 1.
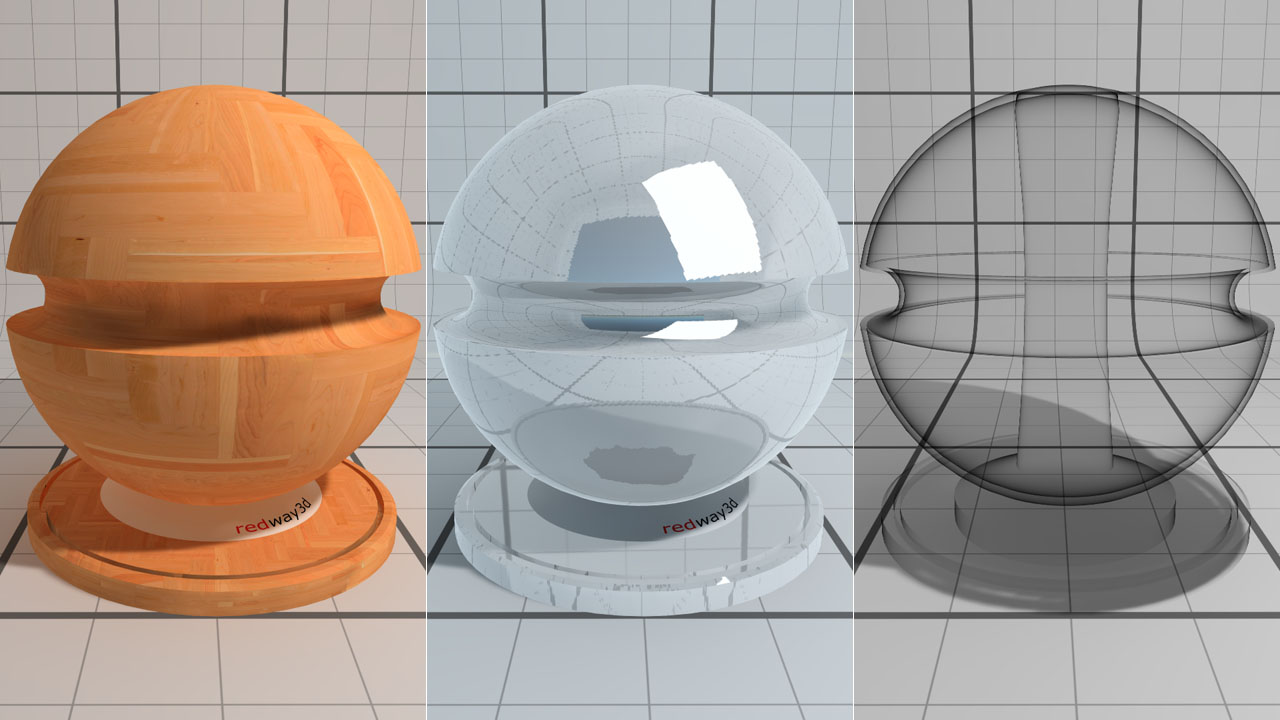
Diffusion, reflection and transmission
More parameters influencing the reflection effect are available like glossiness and IOR (index of refraction).
Increasing the glossiness from 0 to 1
Bump channel
The material also contains:
- Bump: the bump map affects the surface normal of the geometry at the shaded fragment.
Adding bump texture
Back diffuse and translucency
Two more channels are available for plants only:
- Back diffusion: same as diffusion but for the back side faces as defined by the normals.
- Translucency: how much of the back diffusion is visible versus the front diffusion.
These two channels are very useful to render plant leafs.
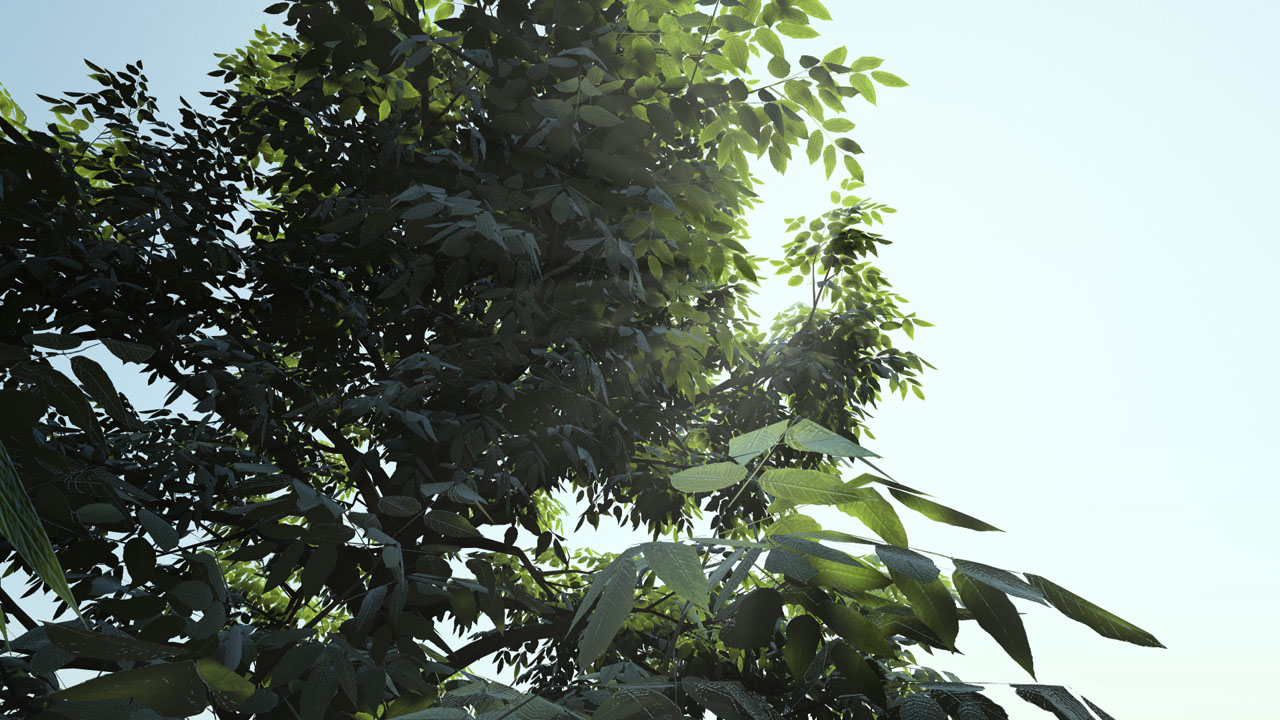

Plant leafs with back diffuse and translucency
Masked material
The material can be defined as masked. In this case, the transmission texture is used as a mask. A property allows to set the alpha threshold over which the geometry is masked.
Decal material
The material can toggle the "decal" check box in its properties. Decal materials are a specific type of materials designed to be applied over other opaque objects. For instance, they're used for road surface markings as explained here: Roads.
Transparency and masking behavior
The realistic material has several data channels such as the transmission, back diffusion and translucency that may trigger some specific behaviors depending on the way the material is used. This short paragraph will explain all cases.
A material can be applied to Plants or to Geometries. Depending on the targeted object, the behavior will differ:
When applying a material to a geometry:
- The back diffusion and translucency channels are ignored. These channels are specific to plant and thus aren't handled when the material is applied to a geometry.
- The transmission defines a true transparency amount, so the resulting opacity of the material can be modified smoothly.
- The "masked / double sided" check box turns a transmission map into a alpha mask map with an alpha threshold defined in the material too.
- A transparent material is single sided and its geometry can only be seen from one side. When the "masked / double sided" button is checked, then the geometry can be seen both ways.
- A transparent material does not cast shadows.
- A masked material casts shadows.
When applying a material to a plant:
- Setting up a transmission map (or value) will turn the material double sided automatically.
- The back diffusion and translucency channels are supported as soon as the material has some transmission.
- The "masked / double sided" button has no effect.
- The material always casts shadows.
 Materials Materials | The PBR metallic material |